Comparing Outdoor Heater for Greenhouse: Electric vs. Propane

Overview
This article compares electric and propane outdoor heaters for greenhouses, highlighting their features, advantages, and benefits to assist users in making informed decisions.
- Propane heaters typically have lower operational costs and provide quicker heat output, which can be advantageous for immediate heating needs.
- On the other hand, electric heaters offer cleaner, emission-free heating and easier installation, making them a suitable choice for those prioritizing environmental factors.
Ultimately, the decision between electric and propane heaters depends on specific greenhouse needs and local conditions.
Introduction
In the realm of greenhouse cultivation, maintaining the right temperature is crucial; it can determine whether the harvest is bountiful or disappointing. As the demand for sustainable and efficient farming practices escalates, understanding the heating needs of greenhouses becomes essential. This article explores the intricacies of greenhouse heating solutions, comparing electric and propane systems, while highlighting their respective benefits and limitations.
Consider the influence of greenhouse size and local climate, along with the specific requirements of various plant species. A comprehensive analysis reveals that the right heating strategy not only supports plant health but also enhances energy efficiency and reduces operational costs. As growers evaluate their options, insights into effective heating management will empower them to make informed decisions that foster optimal growing conditions.
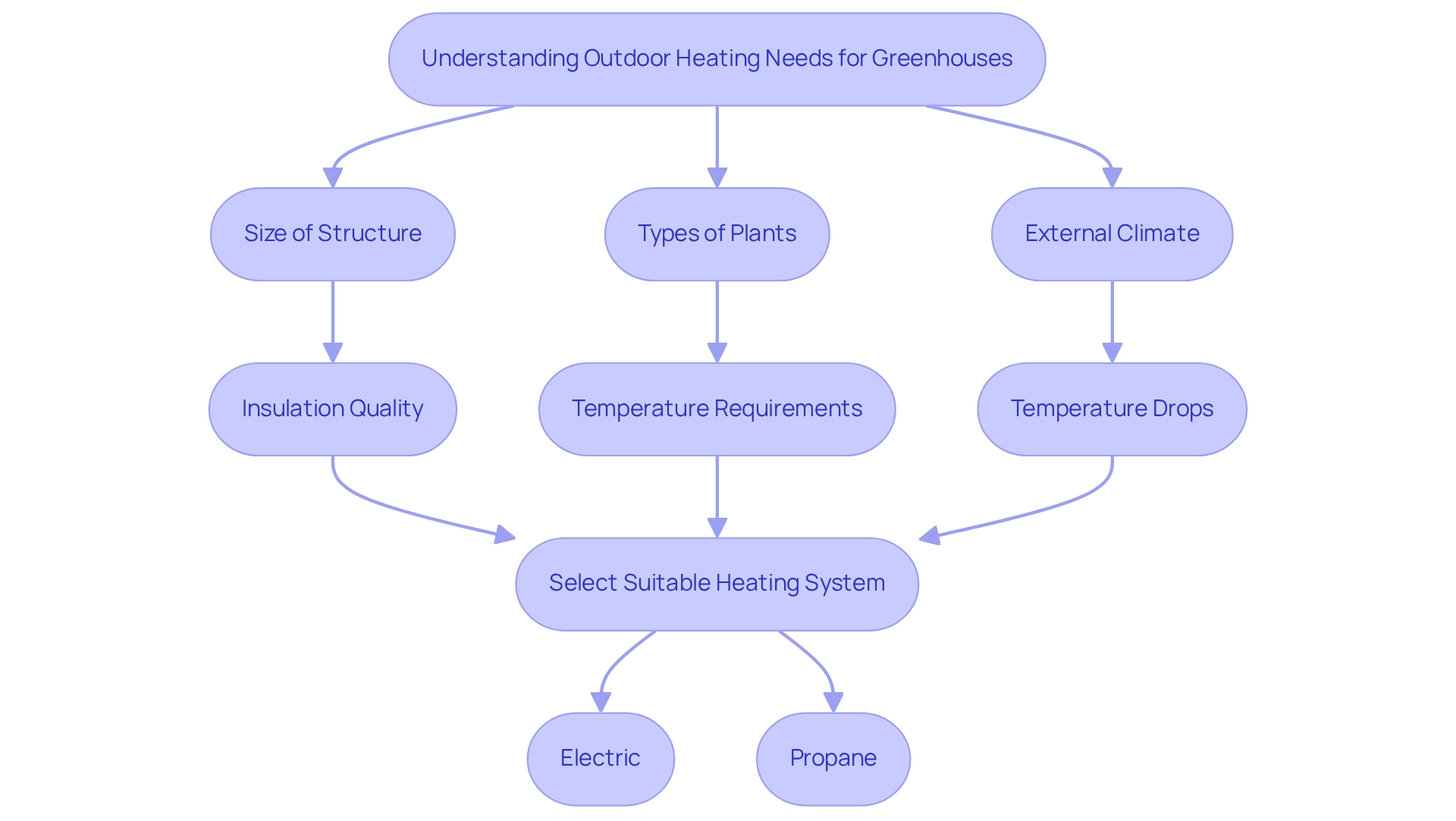
Understanding Outdoor Heating Needs for Greenhouses
Greenhouses require consistent and sufficient warmth to establish ideal growing conditions for plants. Several factors influence warmth needs, including the size of the structure, the types of plants being grown, and the external climate. Larger plant shelters typically necessitate more robust heating systems to maintain steady temperatures, particularly in cooler regions. For instance, older buildings with poor insulation may experience air exchanges of 2.00 to 4.0 per hour, significantly reducing energy efficiency. This suggests that if a greenhouse loses heat rapidly, a more powerful heating system will be essential to compensate for the lost warmth, making the selection of the heating system a critical decision.
Furthermore, specific plants often have distinct temperature requirements that necessitate precise temperature regulation. As J. A. Watson, an assistant professor in Agricultural and Biological Engineering, emphasizes, “Temperature control can be essential to the success of this kind of operation.” This underscores the importance of selecting the right thermal system—whether electric or propane—to ensure plant health and growth efficiency, particularly for sensitive species that thrive within narrow temperature ranges.
Effective strategies for maintaining warmth in plant cultivation must also consider the local climate. In regions with significant temperature drops, efficient heating systems should be designed for future growth and equipped with automatic controls for ease of use. For example, systems featuring thermostats can provide the accurate temperature regulation necessary for optimal plant growth. Implementing these recommendations can enhance the reliability and efficiency of plant growth systems, ultimately leading to improved crop yields and reduced energy costs. Understanding these warmth requirements is crucial for making informed choices about the most suitable solutions for your plant space, especially when evaluating options like an outdoor heater for greenhouse that includes thermostatic controls for ideal temperature regulation.
Exploring Electric Heaters: Benefits and Limitations
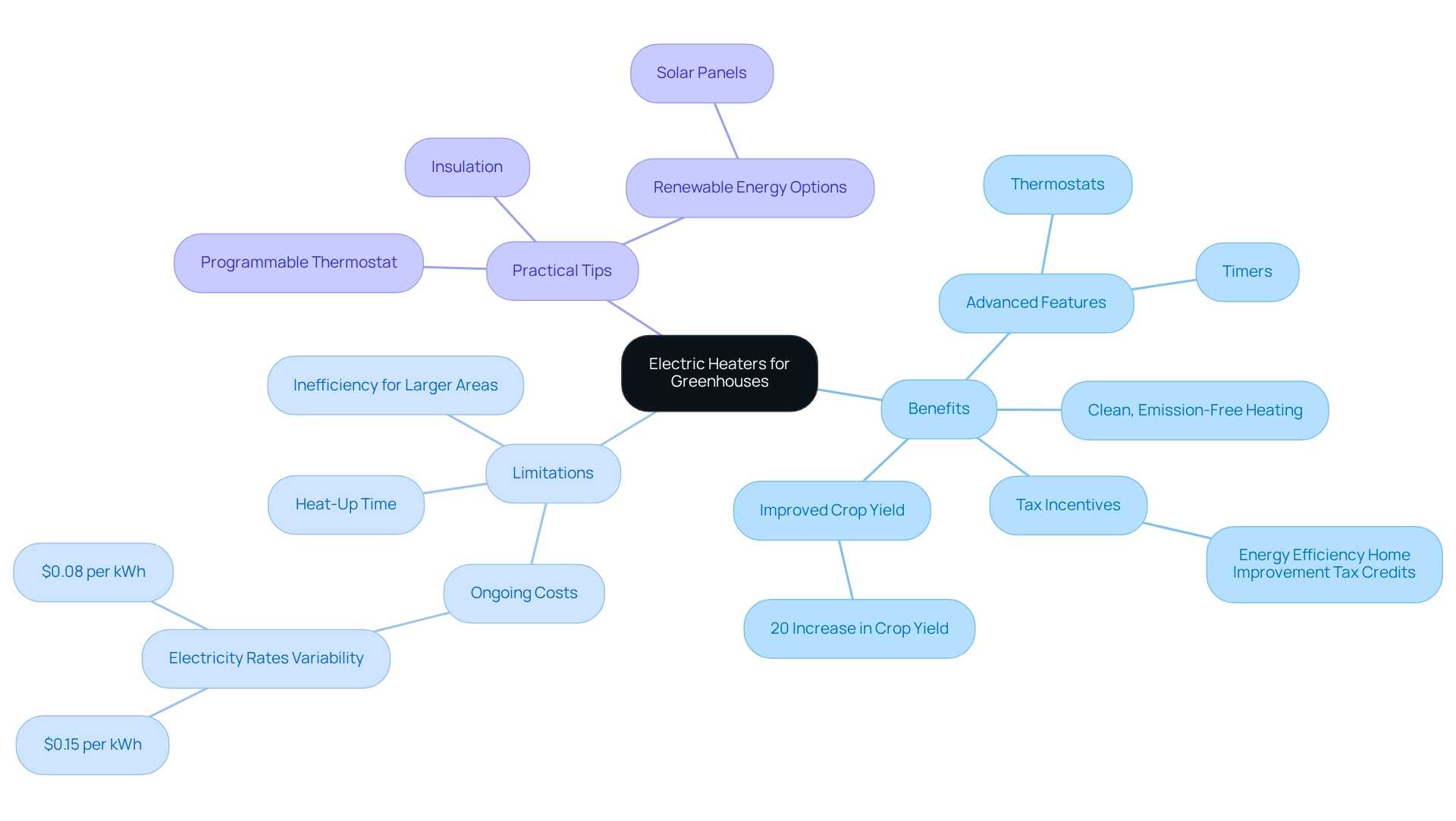
An outdoor heater for greenhouse is increasingly favored for providing warmth due to its straightforward installation and user-friendly operation. They provide clean, emission-free heating, making an outdoor heater for greenhouse use an environmentally friendly option that aligns with eco-conscious living practices. Many models come equipped with advanced features such as thermostats and timers, allowing for precise temperature control, which is vital for plant health. For budget-conscious buyers, energy-efficient home renovation tax incentives from the Inflation Reduction Act can help mitigate initial costs.
Nevertheless, the ongoing expenses associated with powered warming devices can raise concerns, particularly in regions with high electricity rates. For example, average operational costs can differ significantly across various locations, influencing overall affordability. Specific data reveals that, in some areas, operational costs can reach as high as $0.15 per kWh, while in others, they may decrease to $0.08 per kWh. This variability underscores the importance for consumers to assess their local rates, especially when choosing an outdoor heater for greenhouse, as electric warming devices offer convenience and control but typically have a slower heat-up time compared to propane units. This can be a disadvantage in environments where temperatures fluctuate rapidly, potentially affecting the immediate comfort of plants during sudden cold snaps. Additionally, the use of an outdoor heater for greenhouse settings may face limitations in larger plant cultivation areas where substantial warmth is required, possibly leading to inefficiencies. Despite these challenges, the benefits of utilizing this form of warmth in plant cultivation settings are considerable. The use of an outdoor heater for greenhouse contributes to a stable growing environment, which is crucial for maximizing crop yields. Case studies indicate that structures employing powered warming devices have shown improved plant growth and reduced energy consumption over time. For instance, a recent study found that structures using powered warming systems experienced a 20% increase in crop yield compared to those using conventional warming methods. Furthermore, as energy-saving technologies become more widely adopted, powered systems such as outdoor heaters for greenhouses are becoming increasingly economical, aligning with the growing trend of sustainability in agriculture. Statistics show that the market for electric warmers is on the rise, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2% for related warming solutions. This growth reflects a broader shift towards energy-efficient warming solutions in the horticultural sector. Environmental advocates endorse these warming solutions, highlighting their potential to reduce carbon footprints when powered by renewable energy sources.
To enhance eco-friendliness, consider implementing the following practical tips alongside the use of these devices:
- Use a programmable thermostat to optimize heating schedules and reduce energy consumption.
- Insulate your plant shelter to minimize heat loss, ensuring that the device operates efficiently.
- Explore renewable energy options, such as solar panels, to power your device, further lowering your carbon footprint.
In summary, while these warming devices have certain limitations, their benefits in providing controlled, clean warmth make them an appealing choice for plant shelter owners seeking to adopt more sustainable practices.
Examining Propane Heaters: Pros and Cons
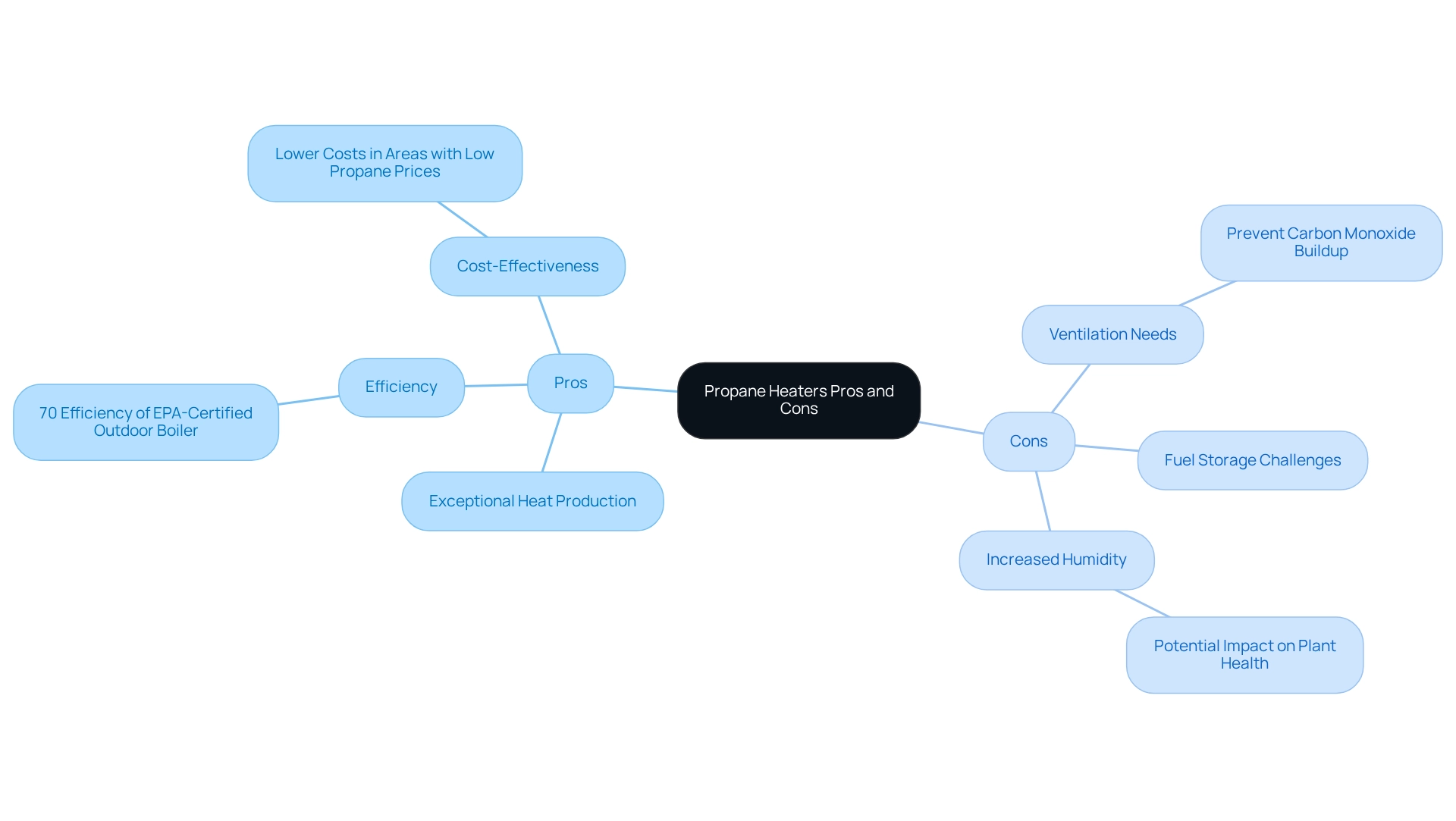
Propane devices are recognized for their exceptional heat production and efficiency, making them an excellent choice as an outdoor heater for greenhouse use, particularly in larger greenhouses or those situated in colder climates. They can quickly elevate temperatures and often prove to be more economical than electric heaters, particularly in areas where propane prices are lower than electricity rates. For example, the efficiency of a new EPA-certified outdoor boiler is estimated at 70%, highlighting the effectiveness of propane heating solutions.
However, it is essential to consider some notable drawbacks. Adequate ventilation is vital to prevent carbon monoxide buildup, necessitating careful planning in the design of the structure. Additionally, propane devices require fuel storage, which can present logistical challenges. While they provide immediate warmth, they may also increase humidity levels within the greenhouse, potentially impacting plant health depending on the species being cultivated.
Expert opinions underscore the importance of selecting the right-sized appliance to optimize performance. Jamie Tuinstra, a Regional Sales Manager at Modine, states, “The appropriate size device makes all the difference in creating a thriving, productive growing environment.” This emphasizes the need for plant cultivation operators to thoroughly assess their specific heating requirements. Seeking expert advice on warming solutions can provide valuable insights regarding the appropriate size and type of device, ensuring optimal operation and plant vitality during the winter months.
In conclusion, while an outdoor heater for greenhouse applications, such as propane heaters, offers significant advantages for growing spaces, including rapid temperature regulation and cost efficiency, it is crucial to acknowledge their limitations for effective management. Furthermore, exploring alternative heating solutions like biomass energy and energy-efficient wood heating may provide additional insights for budget-conscious operators of plant cultivation facilities. A comparison of the average costs of propane versus electricity for heating plant shelters can also aid in making informed decisions, ensuring that growers select the most cost-effective solution for their needs.
Comparative Analysis: Electric vs. Propane Heaters for Greenhouses
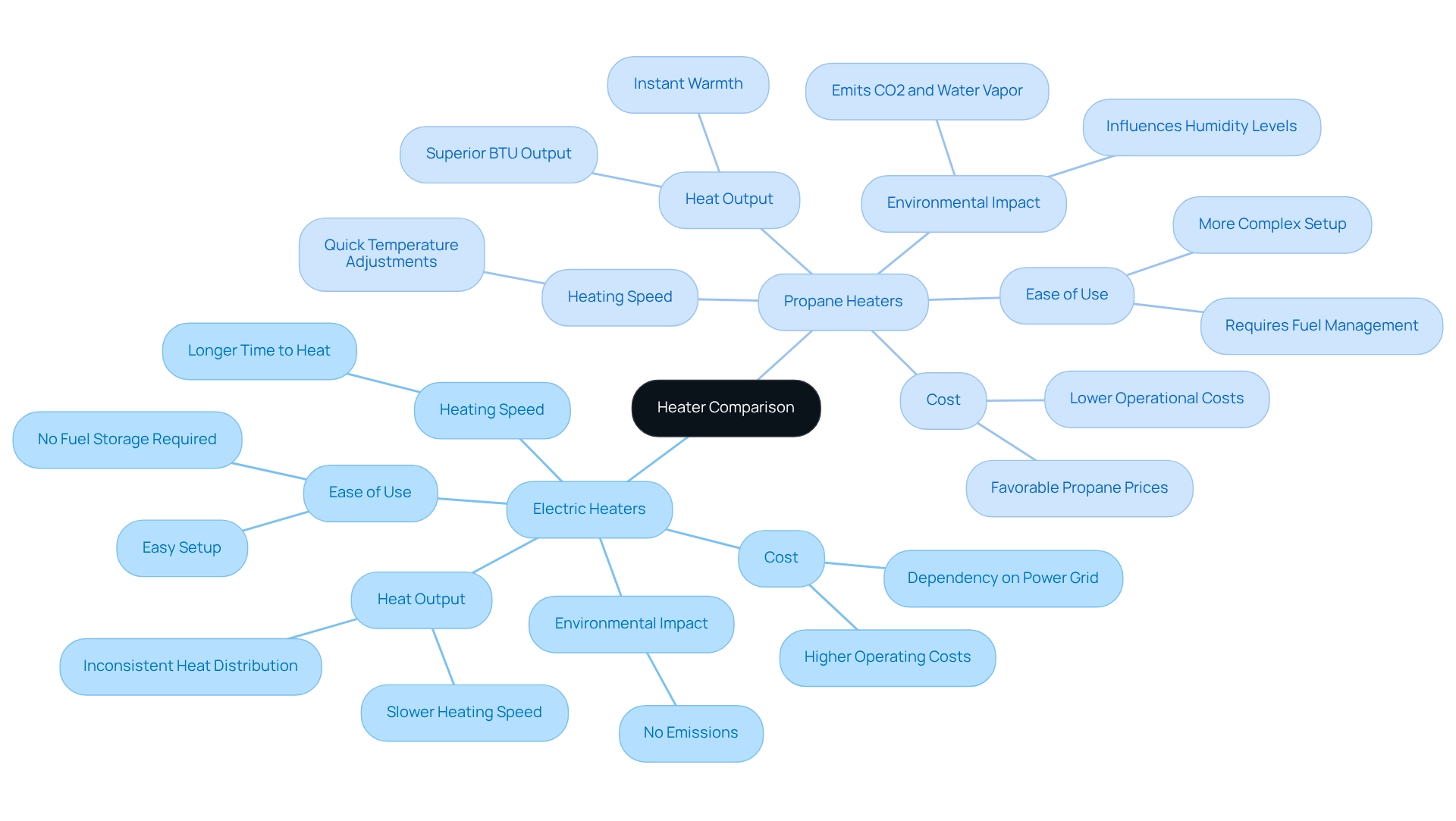
In comparing electric and propane heaters for greenhouses, several critical factors emerge:
-
Cost: Propane heaters typically exhibit lower operational costs, particularly in regions where propane prices are more favorable than electricity rates. For example, a 100-watt light bulb consumes 2.4 kWh in 24 hours, equating to 9/100th of a gallon of propane. This cost advantage can significantly influence long-term budgeting for cultivation operations.
-
Heat Output: Recognized for their superior BTU output, propane units are particularly effective for larger areas or during extreme cold conditions. This capability ensures that plants receive adequate warmth, promoting healthy growth even in harsh weather.
-
Environmental Impact: While electric units produce no emissions, propane units do emit carbon dioxide and water vapor, which can influence humidity levels within the plant enclosure. This distinction is crucial for maintaining optimal growing conditions, as excessive humidity can lead to mold and other issues.
-
Ease of Use: Electric devices are generally easier to set up and manage, eliminating the need for fuel storage. Conversely, propane units require ongoing management of fuel supplies, adding complexity to greenhouse upkeep. As noted by HOP Energy, “Electric heating systems depend on the power grid, which can be a significant concern during power outages.”
-
Heating Speed: Propane devices deliver instant warmth, enabling quick temperature adjustments, while electric units may require more time to reach preferred temperatures. This difference can be vital during sudden temperature drops.
Ultimately, the choice between electric and propane heaters depends on specific cultivation requirements, financial considerations, and ecological factors. A thorough cost analysis reveals that while electric systems may seem convenient, they often incur higher operating costs and are vulnerable to power outages, as highlighted in the case study titled “Challenges of Electric Heating Systems.” In contrast, propane systems offer a reliable and cost-effective solution, particularly for those managing larger greenhouse operations.
Conclusion
Understanding the heating needs of greenhouses is essential for achieving optimal plant growth and maximizing crop yields. Various factors, including greenhouse size, plant species, and local climate, significantly influence the choice between electric and propane heating systems. Electric heaters offer environmental benefits and ease of use; however, they may incur higher operational costs and slower heat-up times. In contrast, propane heaters excel in efficiency and heat output, making them ideal for larger or colder greenhouses. Yet, they require careful management to avoid safety hazards and humidity issues.
The comparative analysis of these two heating options highlights that growers must weigh the pros and cons of each system based on their specific circumstances. For budget-conscious operators, understanding the long-term implications of heating costs is critical, as propane may offer a more economical solution in certain regions. Additionally, the environmental impact of each system should be considered, as sustainable practices are becoming increasingly important in agricultural operations.
Ultimately, selecting the right heating strategy involves a careful assessment of individual greenhouse requirements and a commitment to optimizing plant health while managing energy efficiency. By making informed decisions, greenhouse operators can create a thriving environment that not only supports plant growth but also aligns with sustainable farming practices. This approach ensures a fruitful harvest for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is consistent warmth important in greenhouses?
Consistent warmth is essential in greenhouses to establish ideal growing conditions for plants, as it directly influences their health and growth efficiency.
What factors affect the warmth needs of a greenhouse?
The warmth needs of a greenhouse are influenced by the size of the structure, the types of plants being grown, and the external climate.
How does the size of a greenhouse impact the heating system required?
Larger greenhouses typically require more robust heating systems to maintain steady temperatures, especially in cooler regions.
What issues can arise from older greenhouses with poor insulation?
Older greenhouses with poor insulation may experience significant air exchanges (2.00 to 4.0 per hour), which can reduce energy efficiency and lead to rapid heat loss.
Why is temperature control critical for plant health?
Specific plants have distinct temperature requirements, and precise temperature regulation is essential for their success, particularly for sensitive species that thrive within narrow temperature ranges.
What types of heating systems are recommended for greenhouses?
The right thermal system can be either electric or propane, depending on the specific temperature needs of the plants being cultivated.
How should local climate be considered in greenhouse heating systems?
In regions with significant temperature drops, efficient heating systems should be designed for future growth and equipped with automatic controls, such as thermostats, for accurate temperature regulation.
What are the benefits of implementing effective warmth maintenance strategies in greenhouses?
Implementing effective strategies can enhance the reliability and efficiency of plant growth systems, leading to improved crop yields and reduced energy costs.
What should be considered when selecting a heating solution for a greenhouse?
When selecting a heating solution, it is crucial to understand the warmth requirements specific to the plant space and evaluate options like outdoor heaters that include thermostatic controls for ideal temperature regulation.





